Higher education in Lithuania is open to all persons who have completed general secondary education. Higher education institutions are divided into two types: universities and colleges. As in many other countries, these are either state or non-state.
Colleges may provide only first cycle (undergraduate) professional bachelor study programmes oriented towards training for professional activities and leading to a professional Bachelor’s degree or professional qualification.
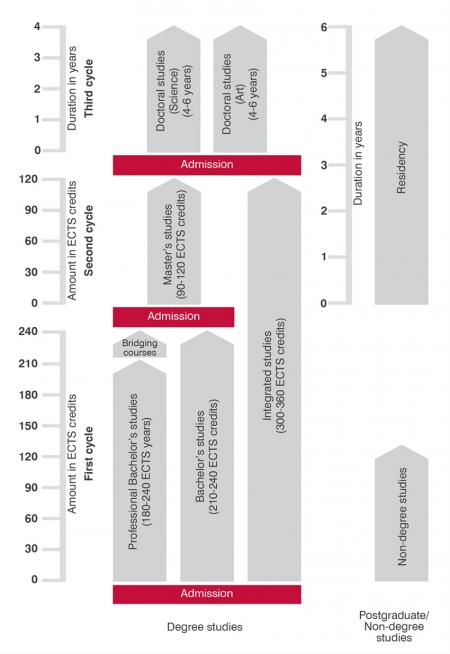
University studies are organized in three cycles: a first cycle of undergraduate studies leading to a Bachelor’s degree (‘Bakalauras’) and lasting three to four years, a second cycle of graduate studies leading to Master’s degree (‘Magistras’) and lasting two years and a third cycle of doctoral studies leading to Doctor’s degree (‘Daktaro mokslo laipsnis’) and lasting for four years.
First cycle (Bachelor’s degree) university study programmes provide universal general education, theoretical preparation and professional capacity of the highest level, and on their completion give access to the second cycle of university studies. Second cycle (Master’s degree) studies are designed to prepare students for careers requiring scientific knowledge and analytical skills and competences. After a Master’s degree is obtained, a student may pursue third cycle (doctoral) studies. Doctor’s degree is awarded after completing doctoral studies and successfully defending a thesis.